Technical Training on WaterMap N-Africa Platform Held in Morocco to Enhance Agricultural Water Resource Management
On 24–25 November 2025, the Aerospace Information Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (AIRCAS), together with the Royal Center for Remote Sensing (CRTS) and Chouaib Doukkali University (UCD), hosted a technical training workshop on “WaterMap N-Africa: Monitoring Platform for Agricultural Water Resources and Water Use in North Africa.” Supported by the Alliance of National and International Science Organizations for the Belt and Road Regions (ANSO) research project, the training took place at the CRTS headquarters in Rabat. This was the second WaterMap N-Africa training offered in the region, following its initial rollout in Tunisia, and attracted over 20 participants from Moroccan research institutions and government agencies engaged in remote sensing, agriculture, and water resource management.
At the opening ceremony, Mr. Rafig AKRAM, Director of CRTS, highlighted that North Africa faces mounting pressures from water scarcity, intensifying climate change, hydrological variability, and growing agricultural water demand. Against this backdrop, he emphasized the urgent need for innovation in Earth observation technologies to develop efficient remote sensing tools, strengthen data monitoring and management, and ultimately improve the accuracy and effectiveness of water resource governance. He encouraged policymakers to actively participate in the program and highlighted the training as a paradigm of China–Africa scientific and technological cooperation. Professor Kamal LABASSI from UCD also addressed the region’s water governance challenges, underscoring the essential role of technological empowerment and international collaboration.
During the workshop, Prof. JIA Li outlined the objectives and framework of the ANSO joint project. Associate Prof. ZHENG Chaolei and Dr. JIANG Min from AIRCAS delivered systematic training on key technologies, including remote sensing–based evapotranspiration (ET) monitoring, estimation of cropland water demand and use, assessment of agricultural Gross Primary Production and Net Primary Productivity (GPP and NPP), and evaluation of water-use efficiency (WUE). They introduced the ETMonitor evapotranspiration model developed by AIRCAS and demonstrated the capabilities of the WaterMap N-Africa platform, which integrates satellite observations with cloud-based data processing.
The hands-on training session enabled participants to practice multi-scale interpretation of remote sensing water-resource products, information extraction, and data analysis. Participants spoke highly of the platform’s technological innovations, particularly its provision of 30-meter high-resolution data, which addresses the long-standing limitation of medium- and low-resolution products in field-scale agricultural applications. The platform’s fine-scale monitoring capability supports a shift from macro-level statistical assessments to field-level precision management, offering strong technical support for the efficient use of agricultural water resources in North Africa.
Notably, Chouaib Doukkali University—co-host of the training—is the hosting institution of the International Center of Excellence (ICoE-El Jadida) under the Digital Belt and Road (DBAR) International Science Program.. Professor LABASSI, who coordinated the training, also serves as the director of ICoE-El Jadida. The center focuses on strengthening regional big-data infrastructure and enhancing sustainable development capacity through big Earth data applications, contributing to improved water resource management and climate resilience. AIRCAS and UCD have collaborated for a long time in the areas of Earth observation, water resources research, and sustainable agricultural development, and this training has further deepened and expanded their partnership.
Developed by the AIRCAS research team led by Prof. JIA Li, the WaterMap N-Africa platform is a core outcome of the ANSO project “Monitoring and Assessment of Water Resources and Agricultural Water Use in North Africa”. Built on web technologies, big Earth data management, and cloud analytics, the platform provides users with 30-meter ET, GPP, NPP, WUE, P-ET, and other agricultural water-resource monitoring products, along with tools for extracting and analyzing spatial–temporal datasets. As a localized system supported by multiple North African institutions, WaterMap N-Africa marks a significant step forward in China–Africa cooperation in Earth observation and agricultural water management. Its promotion and application will offer essential technical support for tackling regional water challenges, improving food security, and addressing climate change—standing as another successful example of international cooperation under the Belt and Road Initiative.

Group photo of the training participants. (Image by AIRCAS)
On-site guidance and interaction during the training session. (Image by AIRCAS)
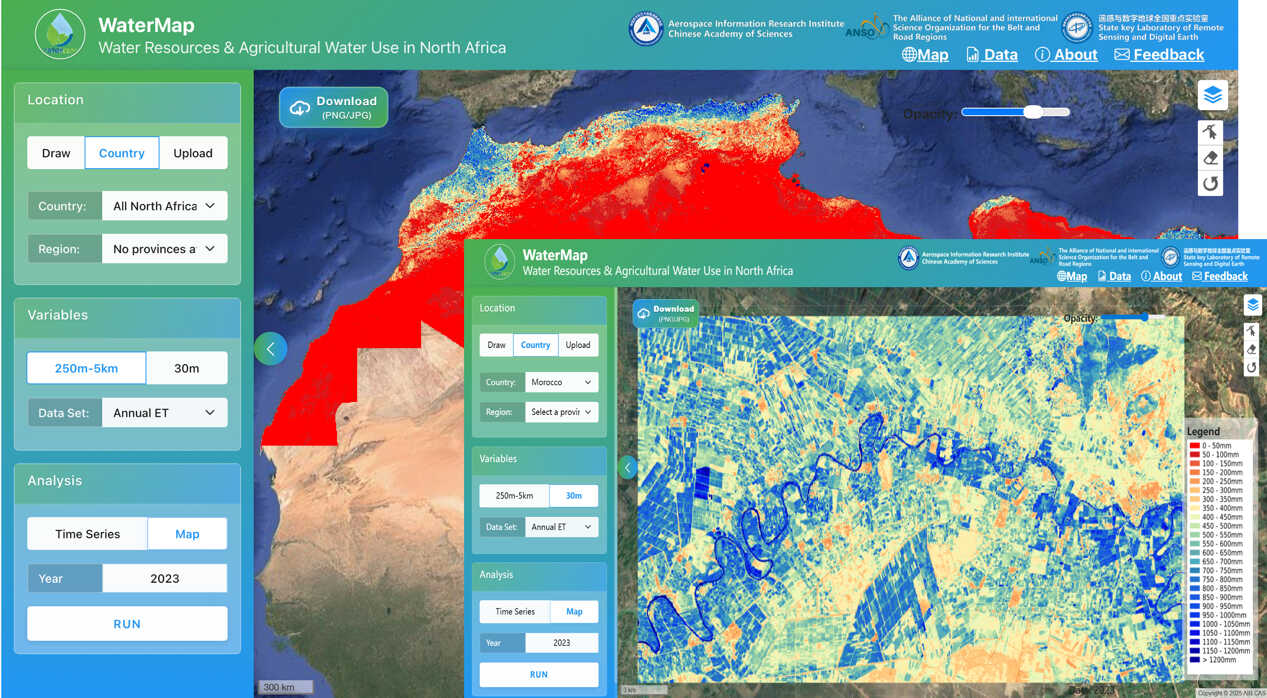
Interface of the WaterMap N-Africa Platform for monitoring agricultural water resources and water use in North Africa. (Image by AIRCAS)



News & Events